Types of Birth Control
bloomwell,
#relationships
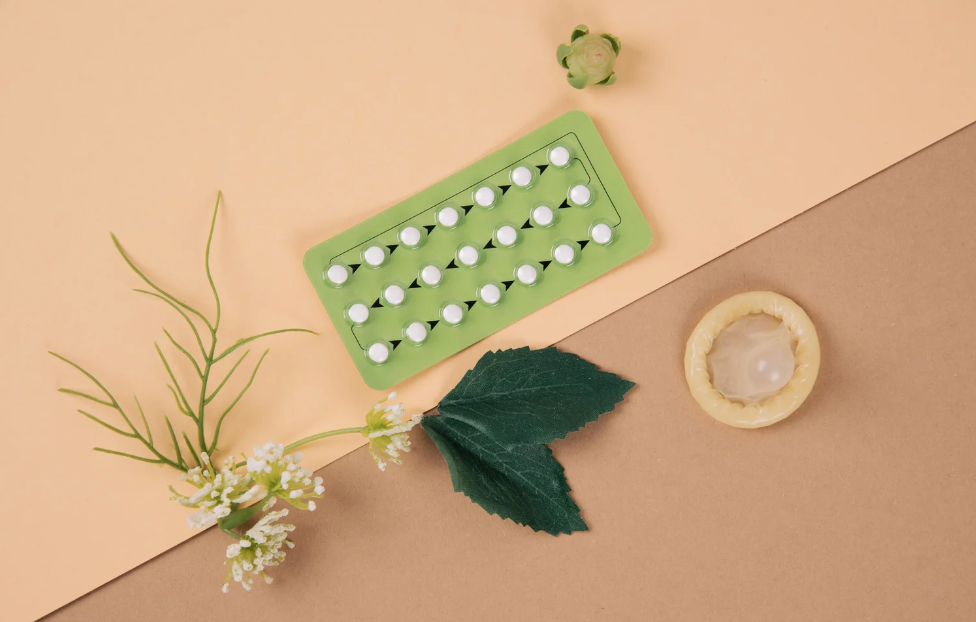

Birth controls are used to prevent pregnancy from sex, below we explain different types of birth control and their effectiveness according to the NHS, it's important to note the effectiveness statistic only if used properly so always follow the instructions on your chosen birth control although we will include some extra bits of advice.
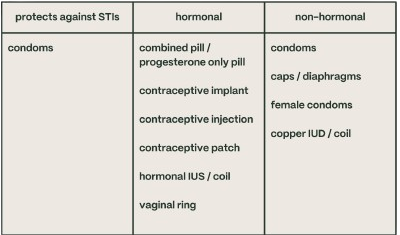
The most common types of birth control are (from NHS):
- condoms
- caps or diaphragms
- combined pill / progestogen-only pill
- contraceptive implant
- IUD (intrauterine device or coil)/ IUS (intrauterine system or hormonal coil)
- contraceptive injection
- contraceptive patch
- female condoms
- vaginal ring
Condoms
Perfect use: 98% effective / Typical use: around 82% effective
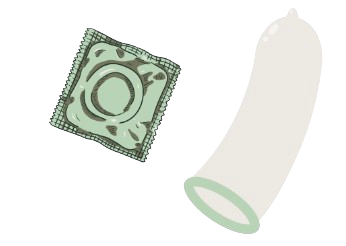 Condoms are the only form of birth control which protect you against sexually transmitted illnesses (STIs). Although other forms of birth control help to protect against pregnancy they do not affect STIs so it's always important to use condoms (even if it's along with side another type of birth control) if you and your partner have not been recently tested.
Condoms are the only form of birth control which protect you against sexually transmitted illnesses (STIs). Although other forms of birth control help to protect against pregnancy they do not affect STIs so it's always important to use condoms (even if it's along with side another type of birth control) if you and your partner have not been recently tested.
Condoms are put on the penis before sex by place them on the top of the penis then rolling down the rest from the outside edges of the circle.
Caps or diaphragms
92-96% effective
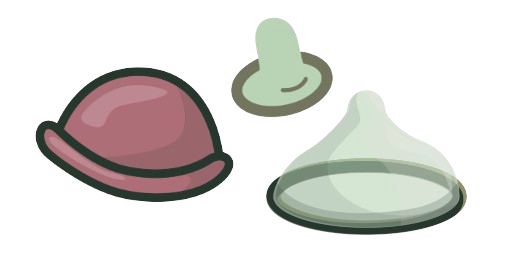 Caps and diaphragms are used with spermicides. Spermicides are usually creams / gels (although they come in other forms) that contain chemicals which kill sperm cells, preventing them from travelling into the uterus. Spermicides can be used alone without caps / diaphragms, however they are much less effective, only about 70%.
Caps and diaphragms are used with spermicides. Spermicides are usually creams / gels (although they come in other forms) that contain chemicals which kill sperm cells, preventing them from travelling into the uterus. Spermicides can be used alone without caps / diaphragms, however they are much less effective, only about 70%.
The spermicide is placed inside the the diaphragm (you need to redo this between sex or if has been over 3 hours) / cap then inserted into the vagina with the spermicide side facing up. Diaphragms are easiest to insert by folding in half then inserting. Always follow the instructions on the diaphragm / cap as they may slightly differ. Using fingers the diagram should be pushed up the vaginal canal as far as it can go, so it will act as a barrier to the cervix (entrance to the uterus).
A diaphragm / cap must stay in place for at least 6 hours after sex, however it is also important to not leave it in for excessive amounts of time or use it on your period to avoid the risk of toxic shock syndrome.
Combined pill / progestogen-only pill
Over 99% effective if used correctly
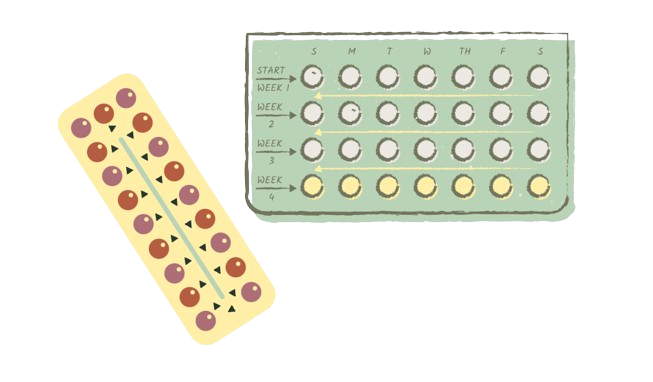 There are many different variations of the combined pill with different ratios of hormones. If you are interested in starting the birth control pill, we recommend you discuss with a doctor which would be best for you, although some times it takes some trial and error to find which one is best suited for you and your body
There are many different variations of the combined pill with different ratios of hormones. If you are interested in starting the birth control pill, we recommend you discuss with a doctor which would be best for you, although some times it takes some trial and error to find which one is best suited for you and your body
The combined pill works by stopping ovulation, preventing eggs from releasing from the ovaries for fertilisation. It also thins the lining of the uterus making it more difficult for a fertilised egg to implant itself.
Contraceptive implant
over 99% effective
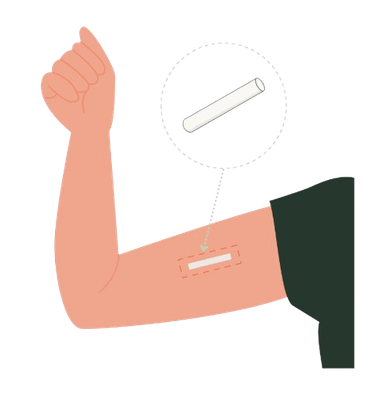 This small plastic rod releases a hormone called progesterone, the same hormone in the pill and that your body naturally produces. By increasing your progesterone levels, ovulation (egg being released) can be prevented and it also thins the lining of the uterus, making it harder for a fertilised egg to implant itself to start a pregnancy.
This small plastic rod releases a hormone called progesterone, the same hormone in the pill and that your body naturally produces. By increasing your progesterone levels, ovulation (egg being released) can be prevented and it also thins the lining of the uterus, making it harder for a fertilised egg to implant itself to start a pregnancy.
This small rod is inserted into the upper arm by a doctor and can last up to 3 years
IUD (intrauterine device or coil)/ IUS (intrauterine system or hormonal coil)
over 99% effective
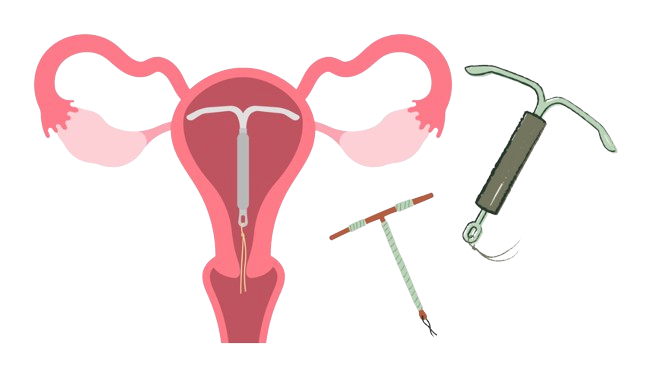 Similar to the implant, a hormonal intrauterine system releases progesterone to prevent pregnancy. However, rather than in the arm this device is inserted directly into the uterus to serve as localised treatment. They can be effective for around 5 years, sometimes longer!
Similar to the implant, a hormonal intrauterine system releases progesterone to prevent pregnancy. However, rather than in the arm this device is inserted directly into the uterus to serve as localised treatment. They can be effective for around 5 years, sometimes longer!
A copper intrauterine device is a non-hormonal option that works by making it harder for sperm to reach an egg as sperm will avoid copper preventing them from swimming to the egg.
Contraceptive injection
over 99% effective
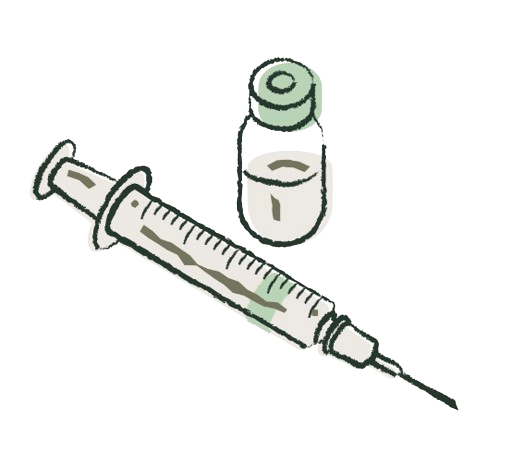 The injection is another method to increase the levels of progesterone in the body to prevent pregnancy.
The injection is another method to increase the levels of progesterone in the body to prevent pregnancy.
Contraceptive patch
Over 99% effective
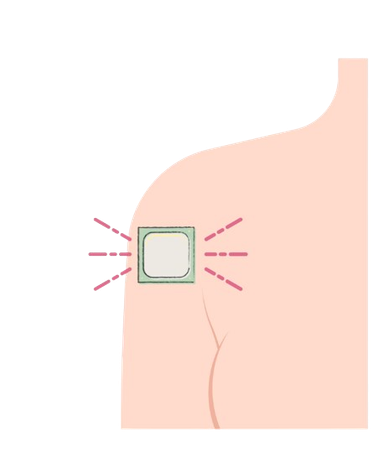 The patch contains oestrogen and progesterone, like the combined pill but enters the body through the skin rather than orally.
The patch contains oestrogen and progesterone, like the combined pill but enters the body through the skin rather than orally.
Female condoms
95% effective
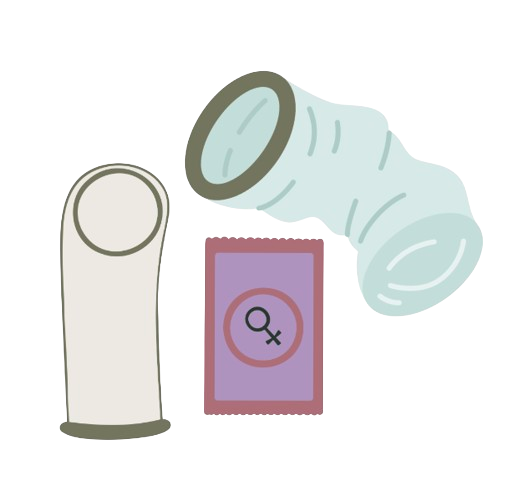 Female condoms are similar to traditionally condoms as they create a barrier preventing sperm from entering the uterus, however they are larger and line the vagina walls rather than holding onto the penis.
Female condoms are similar to traditionally condoms as they create a barrier preventing sperm from entering the uterus, however they are larger and line the vagina walls rather than holding onto the penis.
Vaginal ring
Over 99% effective
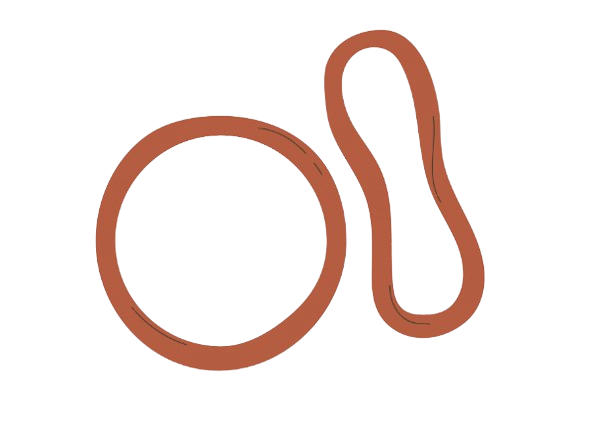 These soft plastic rings also contain oestrogen and progesterone and are inserted into the vagina like a menstrual cup. They can stay there for three weeks then are thrown away and a week break is taken (usually for a period) before inserting a new one.
These soft plastic rings also contain oestrogen and progesterone and are inserted into the vagina like a menstrual cup. They can stay there for three weeks then are thrown away and a week break is taken (usually for a period) before inserting a new one.
Share your thoughts
We're on a mission to bring our community the best content! Loved this article? Got ideas to make it even better or suggestions for future topics? We'd love to hear from you! Your input shapes the future of our content.